Postnatal Treadmill Exercise Alleviates Prenatal Stress-Induced Anxiety in Offspring Rats by Enhancing Cell Proliferation Through 5-Hydroxytryptamine 1A Receptor Activation
Article information
Abstract
Purpose:
Stress during pregnancy is a risk factor for the development of anxiety-related disorders in offspring later in life. The effects of treadmill exercise on anxiety-like behaviors and hippocampal cell proliferation were investigated using rats exposed to prenatal stress.
Methods:
Exposure of pregnant rats to a hunting dog in an enclosed room was used to induce stress. Anxiety-like behaviors of offspring were evaluated using the elevated plus maze test. Immunohistochemistry for the detection of 5-bromo-2ʹ- deoxyuridine and doublecortin (DCX) in the hippocampal dentate gyrus and 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptors (5-HT1A) in the dorsal raphe was conducted. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and tyrosine kinase B (TrkB) levels in the hippocampus were evaluated by western blot analysis.
Results:
Offspring of maternal rats exposed to stress during pregnancy showed anxiety-like behaviors. Offspring also showed reduced expression of BDNF, TrkB, and DCX in the dentate gyrus, decreased cell proliferation in the hippocampus, and reduced 5-HT1A expression in the dorsal raphe. Postnatal treadmill exercise by offspring, but not maternal exercise during pregnancy, enhanced cell proliferation and expression of these proteins.
Conclusions:
Postnatal treadmill exercise ameliorated anxiety-like behaviors in offspring of stressed pregnant rats, and the alleviating effect of exercise on these behaviors is hypothesized to result from enhancement of cell proliferation through 5-HT1A activation in offspring rats.
INTRODUCTION
Stress during pregnancy as well as stress exposure in early postnatal life induces physiological and behavioral changes in offspring [1]. These changes may include the development of anxiety in offspring. Anxiety is accompanied by a constellation of behavioral and physiological defensive responses, including avoidance, vigilance, and arousal [2].
Alterations in markers of neuronal plasticity, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and compromised serotonergic function through alterations in the levels of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) and 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptors (5-HT1A) are implicated in anxiety disorders [3,4]. BDNF is a member of the neurotrophin family, and tyrosine kinase B (TrkB) is its receptor. BDNF and TrkB control neuronal plasticity, and they are associated with many psychological disorders [4-6]. 5-HT is a neurotransmitter involved in the pathogenesis of depression [7]. The 5-HT1A receptor is one of the 5-HT receptor subtypes and is abundantly expressed in the hippocampus. In a study of patients with depression, very low expression of 5-HT1A mRNA was observed [8]. In BDNF-deficient mice, mild stress-induced reduction in hippocampal 5-HT1A receptor expression is prevented by the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, fluoxetine, through activation of TrkB [9]. These results suggest that BDNF expression is closely linked to stress-associated mental disorders [9].
Hippocampal neurogenesis occurs throughout life, including adulthood, and is affected by many environmental factors [10-12]. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis affects learning ability and memory processes, and diverse neuronal markers are expressed during the process of neurogenesis [13]. Among them is doublecortin (DCX), a brain-specific microtubule-associated protein [13]. The hippocampus is involved in cognitive processes and is important in the processing of emotion and modulation of anxiety states [14]. The level of 5-HT synthesis in the dorsal and median raphe plays a key role in mood disorders [15].
Exercise is known to exert beneficial effects on brain function and has been recommended as a useful strategy to manage anxiety and depression [16-18]. In the present study, the effects of treadmill exercise on anxiety-like behaviors and on cell proliferation were investigated using rats exposed to prenatal stress.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals and Treatments
The experimental process was conducted in accordance with the animal care guidelines of the Korean Academy of Medical Sciences and the National Institutes of Health. Pregnant rats were assigned to 3 groups (n=5 in each group): control group, stress-induced group, and stress-induced and exercise group. The offspring were assigned to 4 groups after delivery (n=7 in each group): Offspring in the maternal control group, offspring in the maternal stress group, offspring in the maternal stress with exercise group, and offspring with exercise in the maternal stress group. All offspring received 50 mg/kg of 5-bromo-2ʹ-deoxyuridine (BrdU) intraperitoneally once a day for 2 weeks, 30 minutes before the start of treadmill exercise.
Stress Exposure of Pregnant Rats
Exposure of maternal rats to a hunting dog in an enclosed room was used to induce stress in the pregnant rats, as described previously [17,18]. The exposure time was 10 minutes, and this process was repeated 3 times per day with a 1-hour interval between exposures. This regimen was initiated 7 days after the start of pregnancy and continued until delivery.
Exercise Protocol
Pregnant rats in the stress-induced and exercise group were forced to run on a treadmill for 30 minutes once a day, beginning 7 days after the onset of pregnancy and continuing until delivery. Rats in the offspring with exercise in the maternal stress group were forced to run on a treadmill for 30 minutes once a day, starting 4 weeks after birth and continuing for 4 weeks. Maternal rats and offspring ran at a speed of 2 m/min for the first 5 minutes, 5 m/min for the next 5 minutes, and 8 m/min for the last 20 minutes, at 0° inclination.
Elevated Plus Maze Test
Anxiety-related behaviors were evaluated using the elevated plus maze test as previously described [18]. The elevated plus maze apparatus consisted of two opposing open arms (45 cm×10 cm) and two opposing closed arms (45 cm×10 cm×50 cm), extending from a central platform (10 cm×10 cm) and elevated 65 cm above the floor. The rat was placed on the central platform facing a closed arm and then was allowed to freely explore the maze for 5 minutes. Time spent in the open and in the closed arms was determined.
Tissue Preparation
Offspring were sacrificed 80 weeks after birth, immediately after completing the elevated plus maze test. The rats were anesthetized with Zoletil 50 (10 mg/kg, intraperitoneally; Vibac Laboratories, Carros, France), and 50mM phosphate-buffered saline was perfused transcardially followed by a solution of 4% paraformaldehyde in 100mM phosphate buffer (PB, pH 7.4). Brain coronal sections of 40-μm thickness were prepared using a freezing microtome (Leica, Nussloch, Germany).
Immunohistochemistry for BrdU
BrdU-specific immunohistochemistry in the dentate gyrus was conducted as previously reported [11,19]. Tissue sections were incubated overnight at 4°C with BrdU-specific mouse monoclonal antibody (1:600; Roche, Mannheim, Germany). The sections were then incubated with biotinylated mouse secondary antibody (1:200; Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA) for 1 hour. For visualization, the sections were incubated in 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.6) containing 0.02% diaminobenzide, 40-mg/mL nickel chloride, and 0.03% H2O2 for 5 minutes. After BrdU staining, the differentiation of BrdU-positive cells was evaluated on the same section using a mouse anti-NeuN antibody (1:1,000; Chemicon International, Temecula, CA, USA). Slides were then air-dried overnight at room temperature, and coverslips were mounted using Permount (Fisher Scientific, Fair Lawn, NJ, USA).
Immunohistochemistry for DCX and 5HT1A
Immunohistochemistry for DCX in the dentate gyrus and for 5HT1A in the dorsal raphe was performed as in previous studies [13,19]. Sections were incubated overnight with rabbit antidoublecortin antibody (1 μg/mL; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) or rabbit anti-5-HT1A antibody (1:500; Abcam, Cambridge, UK). Slides were then incubated with biotinylated rabbit secondary antibody (1:200; Vector Laboratories) for one hour. The secondary antibody was amplified with the Vector Elite ABC kit (1:100; Vector Laboratories). Following amplification, slides were air-dried overnight at room temperature, and coverslips were mounted using Permount (Fisher Scientific).
Western Blot for BDNF and TrkB
Expression of BDNF and TrkB was determined by western blot analysis, as described previously [6,20]. Hippocampal tissues were homogenized in lysis buffer. Protein (30 μg) was separated on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, and then transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane. Rabbit anti-BDNF (1:1,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), rabbit anti-TrkB (1:1,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), and mouse anti-β-actin (1:1,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) antibodies were used as primary antibodies. Horseradish peroxidase-conjugated antimouse antibody for β-actin and antirabbit antibody for BDNF and TrkB were used as secondary antibodies.
Data Analysis
The numbers of BrdU-positive and DCX-positive cells in the dentate gyrus were expressed as number of cells per mm2 in the dentate gyrus. Number of 5-HT1A-positive cells in the dorsal raphe was expressed as the number of cells per section. Relative expressions of BDNF and TrkB were measured densitometrically using Molecular Analyst ver. 1.4.1 (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and Duncan post hoc tests. Results are expressed as the mean±standard error of the mean and P-value <0.05 was considered significant.
RESULTS
Effect of Treadmill Exercise on Anxiety-Like Behaviors
Time spent in the open arms was shorter in offspring exposed to prenatal stress compared to offspring not exposed to prenatal stress. Offspring with exercise in the maternal stress group spent more time in the open arms than offspring in the maternal stress group. However, offspring in the maternal stress with exercise group did not spend more time in the open arms (Fig. 1).
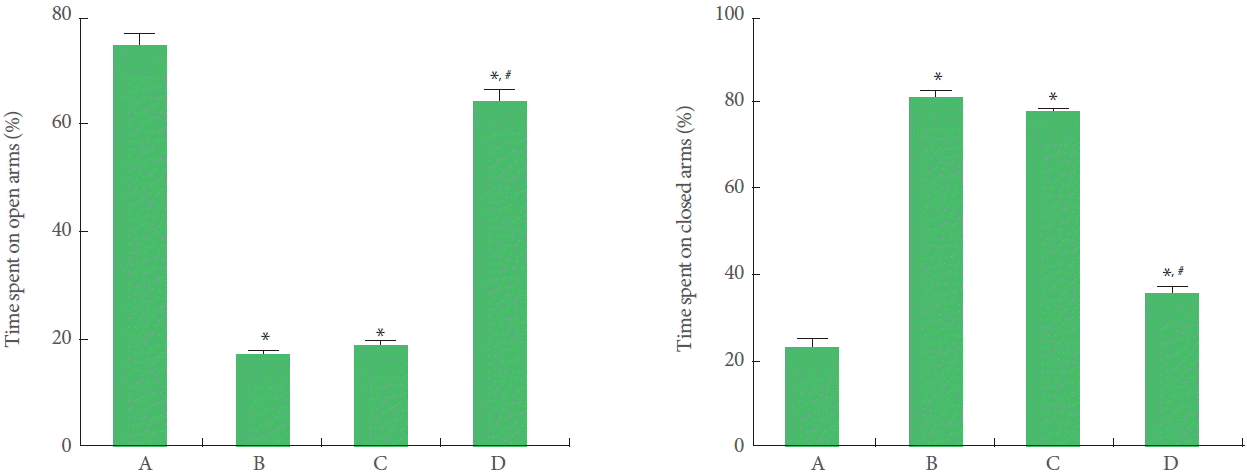
Effect of treadmill exercise on anxiety-like behaviors in the elevated plus maze test. A, Offspring in the maternal control group; B, offspring in the maternal stress group; C, offspring in the maternal stress with exercise group; D, offspring with exercise in the maternal stress group. *P<0.05 compared to the offspring in the maternal control group. #P<0.05 compared to the offspring in the maternal stress group.
Effect of Treadmill Exercise on BDNF and TrkB Expression in Hippocampus
BDNF and TrkB levels were suppressed in offspring exposed to prenatal stress compared to offspring not exposed to prenatal stress (Fig. 2). Offspring with exercise in the maternal stress group showed increased BDNF and TrkB expression than offspring in the maternal stress group. Offspring of the maternal stress with exercise group did not show increased BDNF and TrkB expression.
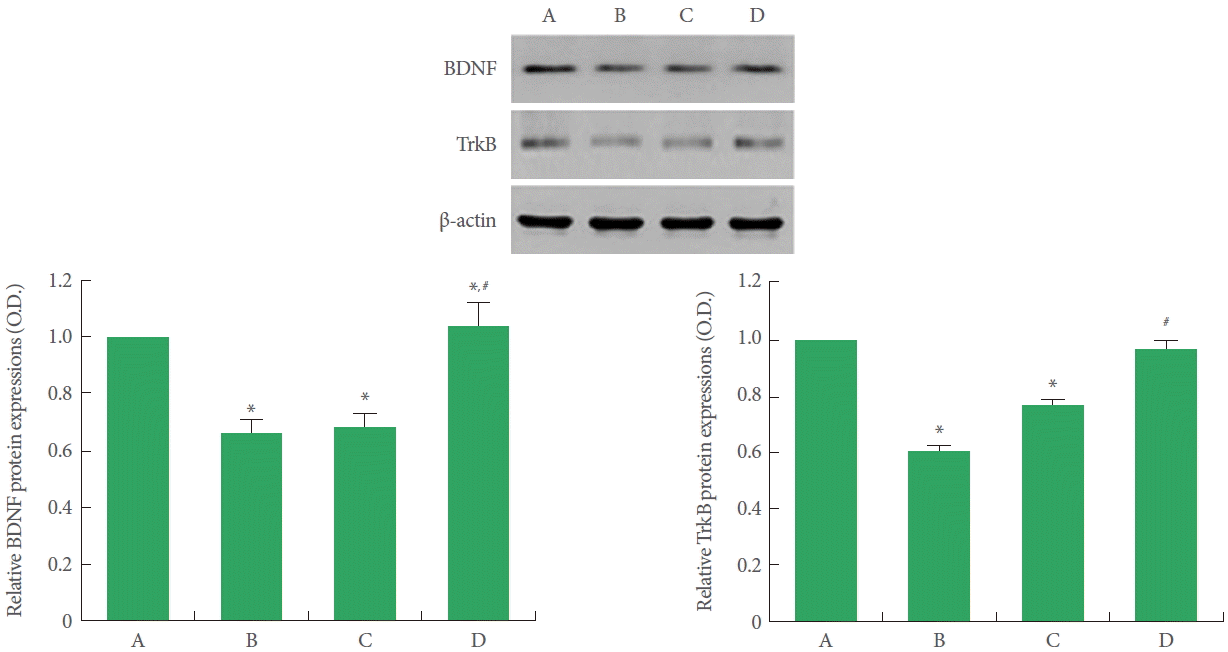
Effect of treadmill exercise on brain-derived neurotrophic factor and tyrosine kinase B expression in the hippocampus. A, Offspring in the maternal control group; B, offspring in the maternal stress group; C, offspring in the maternal stress with exercise group; D, offspring with exercise in the maternal stress group. BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; TrkB, tyrosine kinase B. *P<0.05 compared to the offspring in the maternal control group. #P<0.05 compared to the offspring in the maternal stress group.
Effect of Treadmill Exercise on Cell Proliferation in Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus
Cell proliferation was suppressed in offspring exposed to prenatal stress compared to offspring not exposed to prenatal stress. Offspring with exercise in the maternal stress group showed increases in cell proliferation than offspring in the maternal stress group. Offspring in the maternal stress with exercise group did not show increases in cell proliferation (Fig. 3).
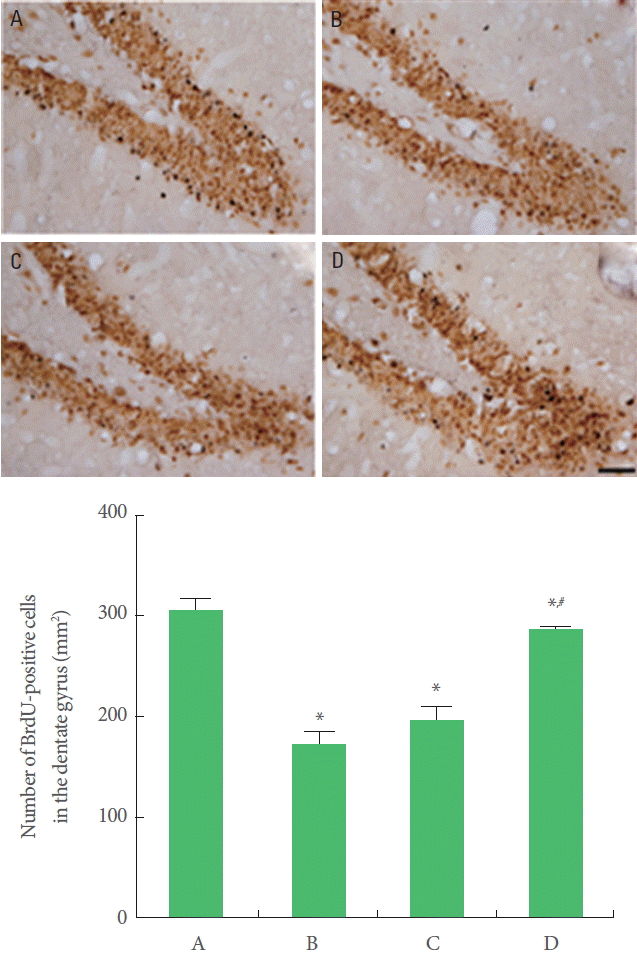
Effect of treadmill exercise on cell proliferation in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Upper: Photomicrographs of 5-bromo-2ʹ-deoxyuridine (BrdU)-positive cells. The scale bar represents 50 µm. Lower: Number of BrdU-positive cells in each group. A, Offspring in the maternal control group; B, offspring in the maternal stress group; C, offspring in the maternal stress with exercise group; D, offspring with exercise in the maternal stress group. *P<0.05 compared to the offspring in the maternal control group. #P<0.05 compared to the offspring in the maternal stress group.
Effect of Treadmill Exercise on DCX Expression in Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus
DCX expression was suppressed in offspring exposed to prenatal stress compared to offspring not exposed to prenatal stress. Offspring with exercise in the maternal stress group showed increases in DCX expression than offspring in the maternal stress group. Offspring in the maternal stress with exercise group did not show increases in DCX expression (Fig. 4).
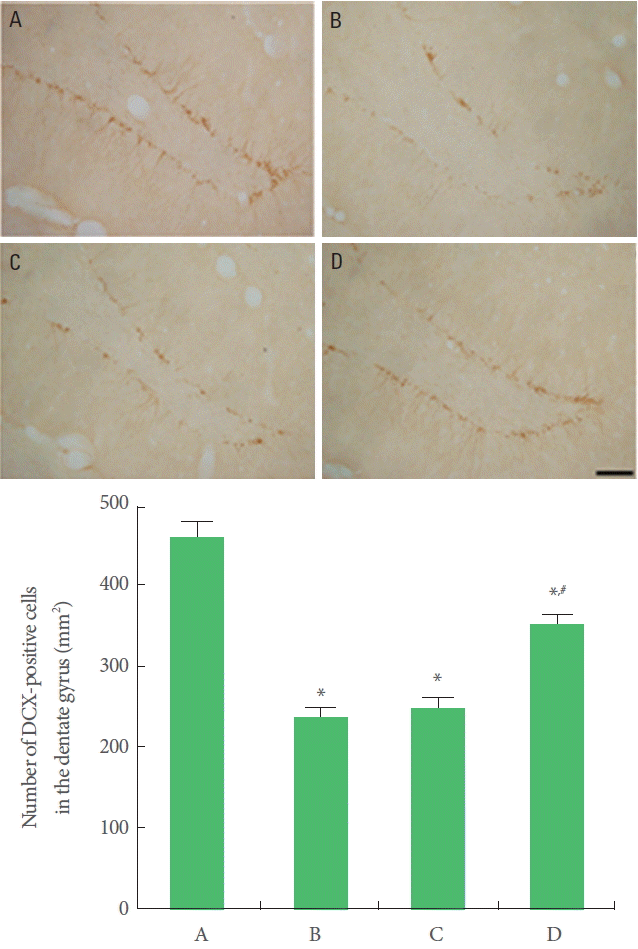
Effect of treadmill exercise on doublecortin (DCX) expression in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Upper: Photomicrographs of DCX-positive cells. The scale bar represents 100 µm. Lower: Number of DCX-positive cells in each group. A, Offspring in the maternal control group; B, offspring in the maternal stress group; C, offspring in the maternal stress with exercise group; D, offspring with exercise in the maternal stress group. *P<0.05 compared to the offspring in the maternal control group. #P<0.05 compared to the offspring in the maternal stress group.
Effect of Treadmill Exercise on 5-HT1A Expression in Dorsal Raphe
5-HT1A expression was decreased in offspring exposed to prenatal stress compared to offspring not exposed to prenatal stress. Offspring with exercise in the maternal stress group showed increases in 5-HT1A expression than offspring in the maternal stress group. Offspring in the maternal stress with exercise group did not show increases in 5-HT1A expression (Fig. 5).
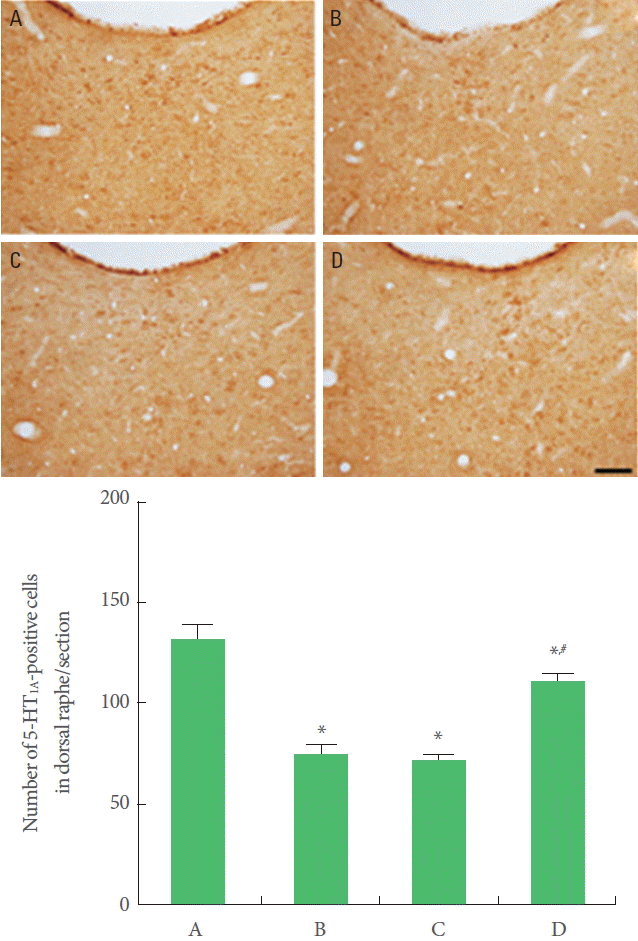
Effect of treadmill exercise on 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor (5-HT1A) expression in the dorsal raphe. Upper: Photomicrographs of 5-HT1A-positive cells. The scale bar represents 100 μm. Lower: The number of 5-HT1A-positive cells in each group. A, Offspring in the maternal control group; B, offspring in the maternal stress group; C, offspring in the maternal stress with exercise group; D, offspring with exercise in the maternal stress group. *P<0.05 compared to the offspring in the maternal control group. #P<0.05 compared to the offspring in the maternal stress group.
DISCUSSION
Prenatal stress is associated with a higher susceptibility to mental illnesses, such as anxiety, which persist throughout postnatal life [21]. The elevated plus maze test is designed to determine the severity of anxiety in rodents, and animals exposed to stress show a reduced duration in the open arms and an increased duration in the closed arms [18]. In this study, rats exposed to prenatal stress spent less time in the open arms and more time in the closed arms, suggesting elevated anxiety-like behavior. Postnatal treadmill exercise by offspring inhibited anxiety-like behaviors as demonstrated in the results from the elevated plus maze. In contrast, maternal treadmill exercise during pregnancy did not inhibit anxiety-like behaviors in offspring.
Prenatal stress is also known to induce alterations in hippocampal synaptic plasticity, demonstrated by suppression of BDNF expression [22] and inhibition of neurogenesis [23]. BDNF-heterozygous mice and mice with impaired hippocampal neurogenesis exhibit anxiety-like behaviors [14,24]. Treadmill exercise reduces anxiety-like behavior and enhances neurogenesis in the hippocampus [25]. Treadmill exercise also increases expression of BDNF in rats with stress-induced depression [26]. In this study, the offspring of rats exposed to stress during pregnancy showed low hippocampal expression of BDNF and TrkB. However, postnatal treadmill exercise increased expressions of BDNF and TrkB in offspring. Similar to behavioral results, maternal treadmill exercise during pregnancy did not affect BDNF and TrkB expression in offspring.
Decreased cell proliferation and suppressed DCX expression in the hippocampus are closely related with many neuropsychological disorders, and treadmill exercise increases cell proliferation and DCX expression, thereby alleviating neuropsychological symptoms [13,18,19,27]. In the present study, the offspring of rats exposed to stress during pregnancy exhibited reduction in cell proliferation and suppression of DCX expression in the hippocampus. Cell proliferation and DCX expression were enhanced when offspring completed the postnatal exercise regimen but were not affected by maternal exercise during pregnancy.
Mood disorders, such as anxiety and depression, are associated with serotonergic dysfunction [28]. 5-HT1A receptor knock-out mice display increased anxiety-like behaviors [3]. Treadmill exercise alleviates stress-evoked impairment of social interaction by enhancing BDNF expression in the hippocampus via activation of 5-HT1A receptors [6]. In this study, offspring of rats exposed to stress during pregnancy showed reduced 5-HT1A expression in the dorsal raphe, but postnatal treadmill exercise enhanced 5-HT1A expression. In contrast, maternal treadmill exercise during pregnancy did not increase 5-HT1A expression in offspring.
The anxiolytic action of treadmill exercise might be related to its effects on serotonergic function [10,29]. Treadmill exercise increases 5-HT synthesis by up-regulation of 5-HT1A receptors, alleviating depressive symptoms caused by stress [29]. Our study shows that offspring born to maternal rats exposed to stress during pregnancy exhibit anxiety-like behaviors, and though maternal treadmill exercise during pregnancy fails to reduce anxiety-like behaviors in offspring, postnatal treadmill exercise ameliorates these behaviors. These results align with hypotheses that treadmill exercise enhances cell proliferation via 5-HT1A activation, thereby alleviating anxiety-like behaviors in rats.
Notes
Grant Support
This work was supported by a Korea University Grant (K1512651).
Conflict of Interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
